Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
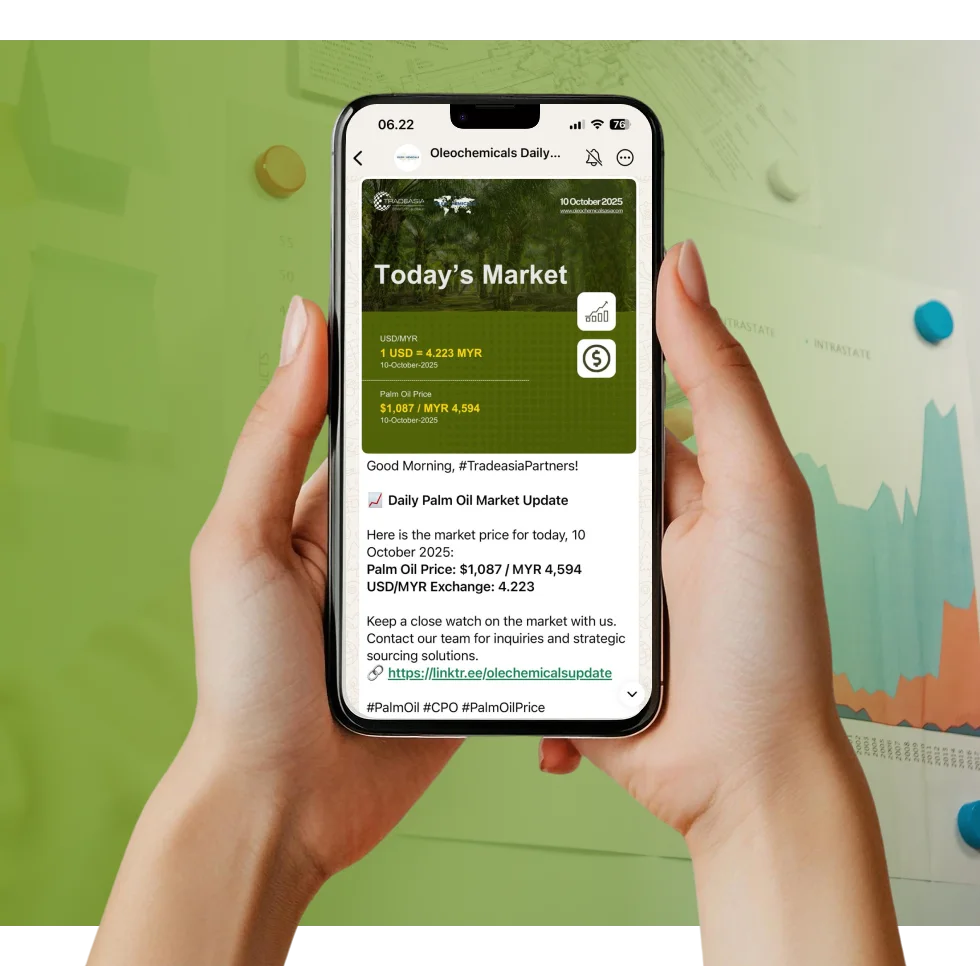
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home Palm Oil-Based Oleochemicals: The Unsung Heroes in Everyday Life
Trade Insights | Application and Buyers | 22 August 2025
Oleochemicals

Invisible yet essential: Palm oil-based oleochemicals are found in daily products like soaps, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and eco-friendly plastics.
Superior efficiency: Palm oil yields more oil per hectare than alternatives, ensuring cost-effective and stable supply chains.
Strong global demand: With 90% of Indonesia’s palm oil exports now in processed form, oleochemicals represent a rapidly growing market.
Sustainable innovation: Bioplastics, biolubricants, and other advanced applications highlight palm-based oleochemicals as key to reducing petrochemical dependency.
Every day, we interact with products made possible by palm oil-based oleochemicals, often without realizing it. From the soap we use each morning to the cosmetics on our shelves and even the eco-friendly plastics shaping a greener future, oleochemicals are everywhere. These compounds, derived primarily from palm oil and palm kernel oil, include fatty acids, fatty alcohols, glycerine, and methyl esters. Together, they form the backbone of countless products across industries ranging from personal care to pharmaceuticals.
The journey from palm oil to oleochemicals begins with processes like hydrolysis and trans-esterification. For instance, crude palm kernel oil can be refined into fatty acids, which then serve as the base for surfactants, emollients, and stabilizers. These components make soaps and detergents highly effective at removing dirt and grease. In cosmetics, oleochemicals act as moisturizers and formulation stabilizers, ensuring creams and lotions deliver both comfort and consistency. Beyond household products, they also play a vital role in pharmaceuticals and serve as renewable building blocks for bioplastics and biolubricants, offering an eco-friendly alternative to petroleum-based chemicals.
What makes palm oil so widely used in oleochemical production is its remarkable efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Palm oil yields more oil per hectare than crops such as soybean or sunflower, making it a far more productive option. Its perennial nature ensures year-round harvests, allowing for a consistent and reliable supply chain that other vegetable oils struggle to match.
From an environmental standpoint, sustainably produced palm-based oleochemicals offer significant benefits. They are biodegradable, renewable, and carry a lower carbon footprint compared to petrochemical counterparts. This combination of affordability, stability, and eco-friendliness positions palm oil as an essential raw material for industries seeking to balance profitability with sustainability.
The demand for palm-based oleochemicals is expanding rapidly as industries seek sustainable solutions. Market forecasts show steady growth, driven by rising consumption in personal care, cleaning products, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. This trend reflects a broader global shift away from fossil fuel-derived chemicals toward renewable, bio-based alternatives.
Indonesia, as one of the world’s largest palm oil producers, is central to this growth. Today, the country produces over 179 types of downstream palm oil products, with oleochemicals making up a significant portion of exports. Notably, around 90% of Indonesia’s palm oil exports now come in processed forms rather than crude oil, underscoring the value-added opportunities in downstream industries like oleochemicals.
The advantages of palm-based oleochemicals ripple across global supply chains. Manufacturers benefit from a cost-efficient, versatile raw material, while consumers enjoy products that are safer, greener, and more effective. Exporters and producers, in turn, capture value from the growing international appetite for biodegradable, renewable ingredients.
Looking ahead, innovation will only expand the possibilities. Research into bioplastics, biolubricants, and other advanced applications promises to further reduce reliance on petrochemicals. This creates a pathway for palm oil to contribute meaningfully to global sustainability goals, supporting industries that are rethinking their environmental impact.
Palm oil-based oleochemicals are more than just industrial inputs—they are a vital part of modern life. Their superior productivity, economic viability, and environmental advantages make them indispensable in today’s global market. As industries worldwide push for sustainable solutions, oleochemicals stand out as a bridge between economic growth and ecological responsibility.
In the years to come, these compounds will continue to shape innovations, ensuring palm oil remains not only a cornerstone of industrial supply chains but also a catalyst for a more sustainable future.
We're committed to your privacy. Tradeasia uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. For more information, check out our privacy policy.
