Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
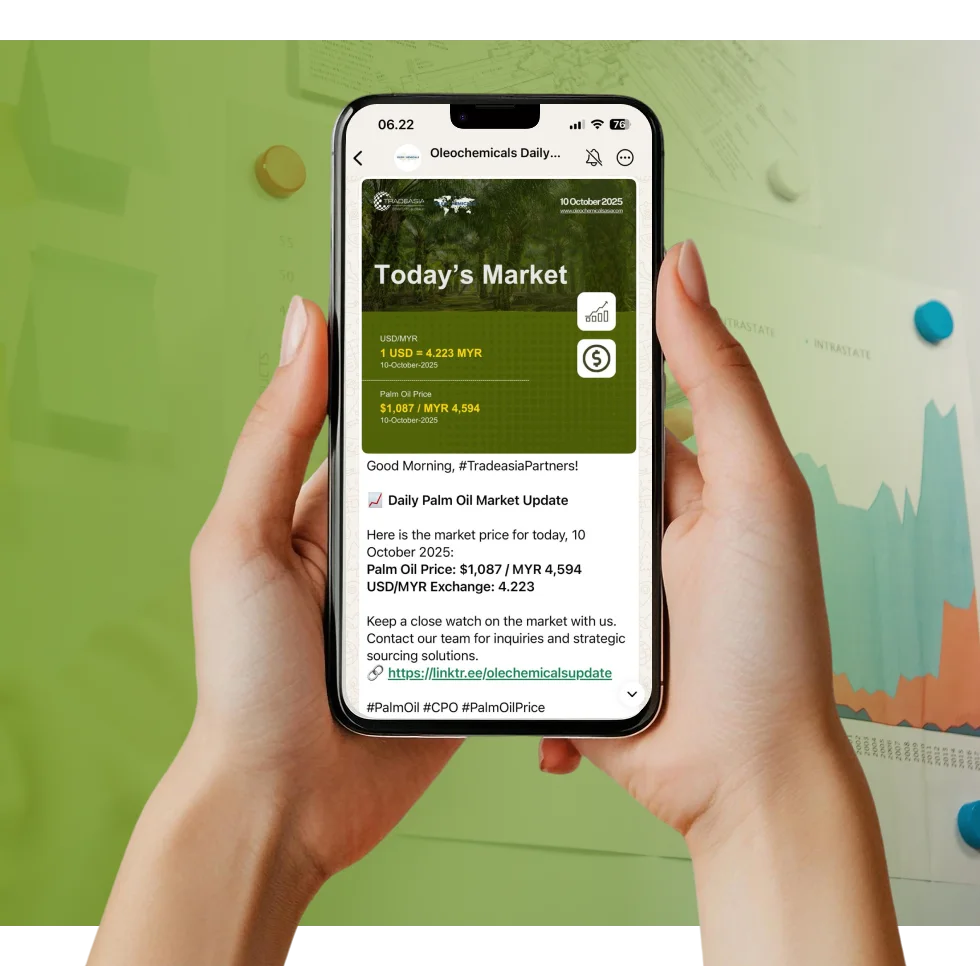
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home From Plantation to Processing: Unlocking Value in Palm Oil Raw Materials
Trade Insights | Supply Chain | 22 August 2025
Oleochemicals

Efficiency gains are crucial – Improved seed varieties and automated mills boost extraction rates to 23–24%, raising output without expanding land use.
Derivatives drive growth – Products like oleochemicals, biofuels, and specialty fats fuel industries from cosmetics to renewable energy, supporting a market expected to exceed 79 million metric tons by 2024.
By-products become assets – Palm kernel shells, fibers, and wastewater can be repurposed into bioenergy and sustainable solutions, reinforcing circular economy practices.
Innovation secures advantage – Robotics, synthetic biology, and digital traceability empower businesses to enhance productivity, meet certification standards, and access premium global markets.
Palm oil has long stood as a cornerstone commodity, playing an indispensable role across food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and countless industrial applications. Yet, in today’s highly competitive and sustainability-driven marketplace, simply producing crude palm oil is no longer enough. For businesses involved in the palm oil supply chain, maximizing value lies in three key strategies: boosting production efficiency, diversifying derivative products, and harnessing by-products sustainably. These pillars not only strengthen profitability but also ensure resilience against market volatility and rising sustainability expectations.
At the plantation level, technology and innovation have dramatically reshaped how palm oil is produced. Advanced seed varieties such as the Musim Mas GS Series can triple yields compared to industry averages, providing higher oil extraction rates while improving resilience against diseases. This means greater productivity per hectare without expanding land use—a crucial step in reducing deforestation and preserving biodiversity.
In processing, modern palm oil mills now run fully mechanized operations capable of handling 3 to 60 tonnes of fresh fruit bunches (FFB) per hour. Energy-efficient boilers fueled by biomass waste from fibers and shells further reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Together, these innovations lift extraction rates to 23–24% per bunch and ensure crude palm oil consistently meets strict international edible oil standards. Such efficiency gains not only cut costs but also position producers more competitively in global markets.
The value of palm oil extends far beyond crude production. Derivative products have become the backbone of downstream industries. Oleochemicals, including fatty acids, glycerin, and related compounds, are essential in producing soaps, detergents, cosmetics, and even pharmaceuticals. Palm-based biofuels are increasingly aligned with renewable energy targets, offering strong growth prospects as governments tighten decarbonization goals.
Additionally, specialty fats derived through fractionation and modification serve high-demand markets such as confectionery, bakery, and food service sectors. Market projections show that global palm oil production will surpass 79 million metric tons by 2024, largely fueled by demand in these value-added applications. By diversifying into derivatives, businesses can create multiple revenue streams and shield themselves from volatility in crude palm oil prices.
Sustainability is no longer optional—it is at the heart of long-term competitiveness in palm oil. By-products like palm kernel shells and fibers, once considered waste, are now being transformed into bioenergy feedstocks that power factory operations. This not only reduces fossil fuel use but also supports circular economy principles.
Meanwhile, wastewater management and advanced treatment technologies are helping mills minimize environmental impact. On the supply chain side, digital innovations such as GIS mapping and blockchain traceability enhance transparency, strengthen compliance with certification standards, and reassure consumers about ethical sourcing. These efforts illustrate how by-products and digital tools together can turn sustainability into a strategic advantage.
The palm oil sector is also embracing cutting-edge innovation. Intelligent robots capable of detecting diseases early protect yields before they are compromised. At the same time, synthetic biology startups are developing palm oil alternatives via microbial fermentation, offering complementary pathways toward sustainability. Companies that integrate precision agriculture and digital monitoring tools gain the ability to optimize input use, track environmental footprints, and ultimately achieve higher productivity with lower impact.
Such forward-looking strategies differentiate producers in an increasingly crowded market. More importantly, they open access to premium global markets where compliance with environmental and ethical standards is non-negotiable.
Maximizing value from palm oil raw materials is no longer just about cultivation. It requires an integrated approach—efficient production, expanded derivative portfolios, and sustainable by-product utilization backed by digital innovation. Businesses that invest in these strategies can capture growth across evolving global markets while aligning with the sustainability mandates that define the industry’s future.
By moving beyond the role of commodity suppliers, palm oil companies have the opportunity to position themselves as key players in a value-driven, innovation-oriented ecosystem that not only delivers profit but also contributes to a more sustainable future.
We're committed to your privacy. Tradeasia uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. For more information, check out our privacy policy.
