Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
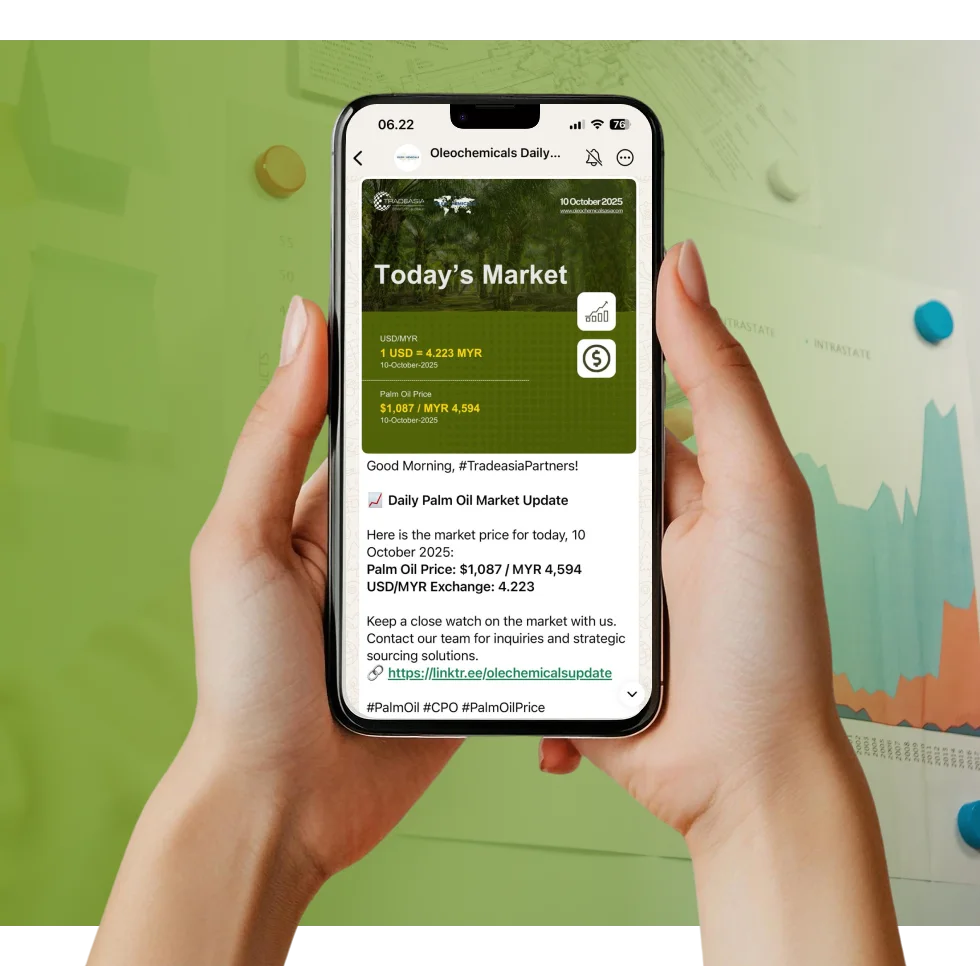
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home From 2020 to 2040: How RBD Palm Oil Shapes the Future of Global Trade
Trade Insights | Supply Chain | 25 August 2025
Oleochemicals

Global Trade Dynamics and Shifting Consumption Patterns
Innovation, Sustainability, and the Road Ahead
Refined, Bleached, and Deodorized (RBD) palm oil has established itself as a cornerstone of international commerce between 2020 and 2040. Dominated by Indonesia and Malaysia, which together supply over 85% of the global market, this commodity is more than just a raw material—it is an economic driver that generates billions in annual export revenues. Its versatility, spanning from food to cosmetics and biofuels, makes it indispensable, and its trajectory reflects how global trade itself is being reshaped.
In the early 2020s, global trade in RBD palm oil experienced steady growth. By 2025, Indonesia’s production reached 48 million tons, while Malaysia stabilized at around 19.5 million tons. The export market proved robust, with values of USD 8.5 billion in 2024 projected to expand to USD 12.3 billion by 2033, representing a 5.1% CAGR beyond 2026. Much of this growth is fueled by Asia-Pacific, where countries like China and India dominate consumption. India alone is expected to import 9.4 million metric tons by 2025, a surge supported by tariff exemptions and rising domestic demand.
Meanwhile, consumption in Europe and Africa has followed different paths. European markets are becoming increasingly selective, with imports of certified sustainable palm oil rising even as overall usage declines. This trend highlights Europe’s shift toward eco-conscious sourcing. Africa, on the other hand, is emerging as a key growth frontier, with rising urbanization and government incentives creating fertile ground for palm oil expansion.
Pricing remains closely tied to supply-demand imbalances and national energy policies. Indonesia’s B35 and B40 biodiesel programs, for example, are expected to absorb 9.6 million metric tons in 2025, tightening export availability and contributing to price volatility. Across regions, the food industry continues to underpin demand, particularly in Asia’s fast-food sectors where RBD palm oil’s affordability and thermal stability keep it central to frying and processed food production. Cosmetics and biofuel applications are also climbing steadily, especially in Europe and Africa, reflecting the product’s growing relevance beyond the food sector.
The resilience of RBD palm oil’s global trade lies not only in demand but also in technological and structural advancements. Trading platforms have been transformed through digitalization, enabling streamlined procurement and more transparent inventory management. Logistics improvements and micro-fulfillment models have reduced lead times, while sustainability certifications such as RSPO and advanced traceability systems have become critical tools in meeting stricter environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
Yet challenges loom large. Climate change poses risks to yield stability and production costs, while price volatility is likely to persist due to biofuel mandates and energy market fluctuations. Geopolitical factors, from EU restrictions to shifting tariffs, will continue to redirect exports toward markets like China and India. These pressures are compounded by the risk of supply chain fragmentation if global markets split between compliant and non-compliant producers.
For palm oil trading companies, the future demands agility. Expanding into emerging regions such as Africa and the Middle East, investing in supply chain transparency, and aligning with sustainable sourcing practices will be crucial to long-term success. The sector’s evolution underscores that RBD palm oil is not merely a commodity but a strategic asset—one that will continue to drive international commerce over the next two decades.
In conclusion, the journey of RBD palm oil from 2020 to 2040 highlights its enduring role in global trade. Its adaptability across industries, combined with technological progress and sustainability commitments, ensures its central place in the international marketplace. However, the future will require strategic foresight, innovation, and resilience to navigate the climate, market, and geopolitical challenges ahead.
We're committed to your privacy. Tradeasia uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. For more information, check out our privacy policy.
