How can we assist you?
Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
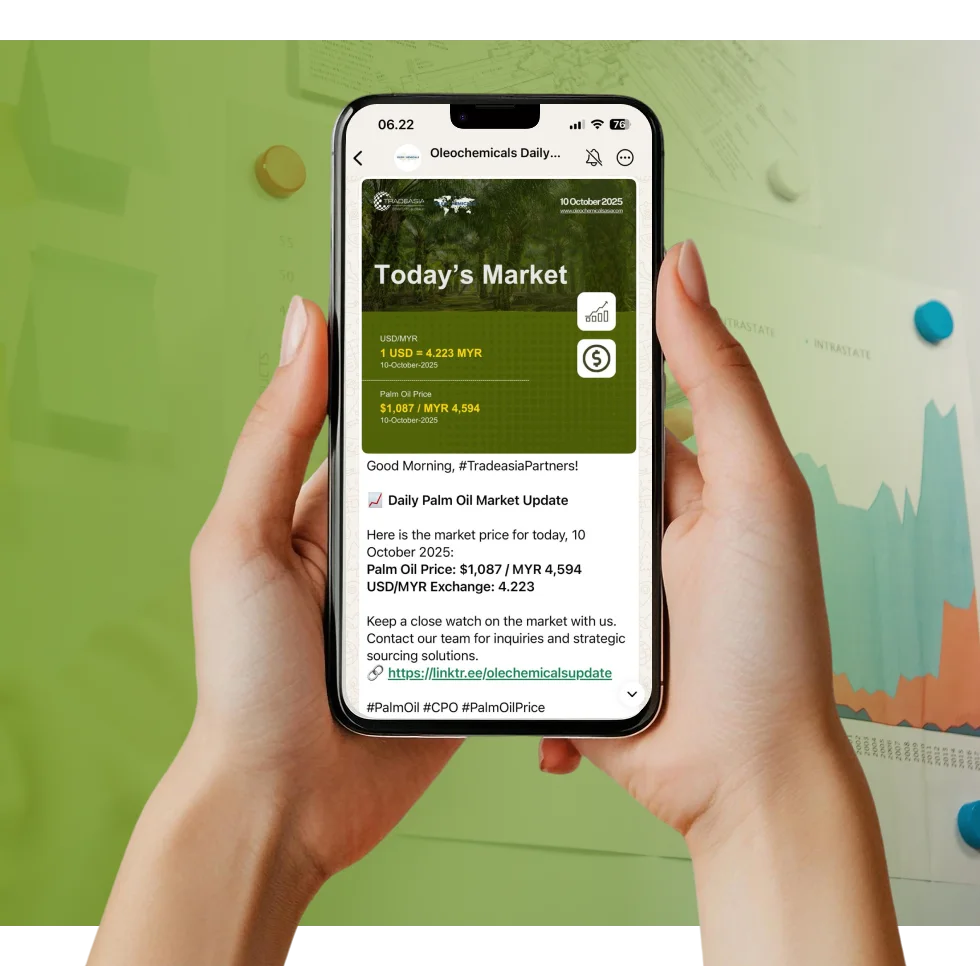
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Log in now to access technical product documents from our product range.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home All Products Crude Glycerine 80% Min Palm Based High MONG
|
Origin |
: Indonesia |
|
IUPAC Name |
: propan-1,2,3-triol |
|
Cas Number |
: 56-81-5 |
|
HS Code |
: 1520.00.00 |
|
Formula |
: C3H8O3 |
|
Appearance Name |
: Light yellow to dark brown, viscous liquid |
|
Common Names |
: Glycerol |
|
Packaging |
: 20 MT / Flexi Bag |
For more detailed information including pricing, customization, and shipping:
Brief Overview
Crude glycerine, characterized by its viscous consistency, innate sweetness, and a chromatic spectrum ranging from light yellow to dark brown, represents the unrefined manifestation of glycerine. It is sourced from both natural and chemical feedstocks, primarily existing in vegetable oils and fats in the form of triglycerides, alongside its presence in animal fats. This byproduct is derived from biodiesel manufacturing plants and oleochemical industries. The shift towards renewable energy sources has induced a notable surge in biodiesel production, consequently amplifying the generation of crude glycerine. The specifications for crude glycerine typically stipulate an 80% glycerine content, with the remaining composition comprising impurities such as methanol, soap, catalyst, salts, non-glycerine organic matter, and water. This intricate interplay of factors underscores the intricate nexus between biodiesel production, renewable energy initiatives, and the resultant crude glycerine byproduct.
Manufacturing Process
Degumming
Degumming is a crucial step in refining vegetable oil, involving precise removal of phosphatides through centrifugation. Water is added to precipitate dissolved phosphatides, which become heavier masses due to absorbed water. Centrifugation then separates these phosphatides, effectively eliminating impurities and refining vegetable oil, extending its storage life.
Deacidification
Deacidification follows, using solvent extraction on vegetable oils. The initial step agitates vegetable oil in methanol, causing free fatty acids to dissolve, reducing their concentration. Removal of these acids is crucial for extending storage time and facilitating further refining.
Transeferication/Saponification
The deacidified oil undergoes transesterification/saponification, breaking triglyceride chains into glycerol/glycerine and fatty acids. This step, conducted under high temperature and pressure with water, makes glycerine accessible for extraction, setting the stage for additional refinement.
Feedstock
Crude glycerine has a high metabolizable–digestible energy ratio that is similar to soybean oil's. For farms that breed cattle and other herbivorous animals, glycerine provides a source of energy.
Chemical intermediate
Remaining crude glycerine is transformed into an intermediate molecule via thermochemical processes. Propylene glycol, the final product of hydrogenolysis, can be generated by refining crude glycerine. Propylene glycol, often referred to as glycol, has two roles in the world of methanol-powered cars: it is an essential component of antifreeze formulations and a fuel additive.
Composting
By means of several biological transformations, crude glycerine can be utilized in composting. Anaerobiospirillum succinic, a bacteria, ferments crude glycerine to create succinic acid as the end product. Furthermore, additional investigation has revealed that the fermentation of algae might produce omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids from crude glycerine.
How can we assist you?
