How can we assist you?
Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
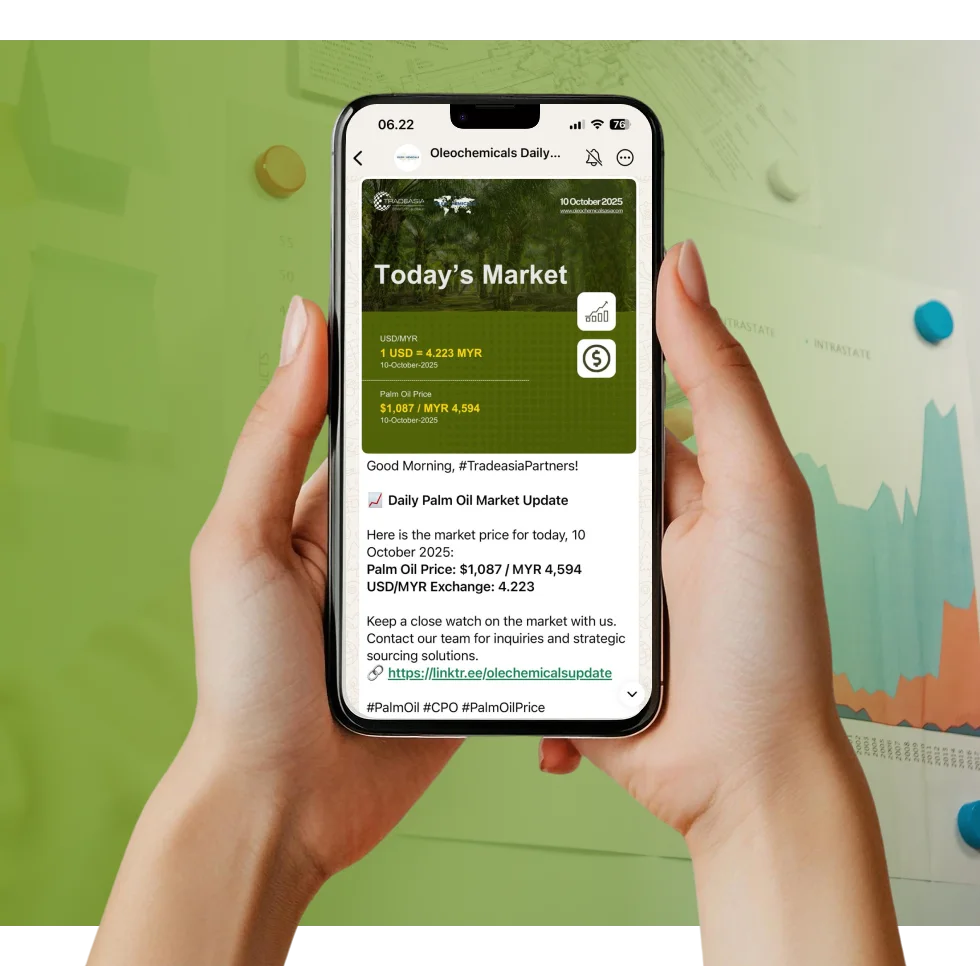
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home Beyond 99%: How Biocatalyst R&D is Delivering Cheaper, Purer (99.9%+) Methyl Stearate
Article | 27 October 2025
Oleochemicals

For decades, the production of Methyl Stearate has been a "brute force" chemical process. The industry standard has relied on chemical catalysts like sodium methoxide, which require high temperatures (often >100°C) and high pressure to function. This method is not only energy-intensive but also creates soap byproducts, limiting the final purity to a standard 98.5% grade and requiring costly, water-intensive purification steps.
This production evolution is creating new opportunities, but also new complexities in the supply chain. At Tradeasia International, we thrive on this complexity. Our job is to connect our partners directly to these process innovations, ensuring they source not just a product, but the right product—whether it's a standard grade or a new, high-purity sustainable ester.
Cutting-edge R&D is now decisively shifting away from this old model and toward biocatalysis. By replacing harsh chemical catalysts with immobilized lipase enzymes, manufacturers can now run the esterification process at much lower, near-ambient temperatures (around 50-60°C). This single change is a game-changer for sustainability, as it can reduce the process's total energy consumption by up to 40%.
The benefits go far beyond simple energy savings. The high specificity of enzymes virtually eliminates the formation of soap and other byproducts. This allows producers to achieve an unprecedented 99.9%+ purity in a single step, creating a food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade product without the need for costly distillation. Furthermore, these robust enzymes can often be reused for over 200 production cycles, slashing catalyst costs and waste generation. For buyers, this R&D wave means high-purity, "green" Methyl Stearate—with a 25% lower carbon footprint—is moving from a high-cost specialty to an accessible, competitive standard.
Sources:
We're committed to your privacy. Tradeasia uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. For more information, check out our privacy policy.
How can we assist you?
