How can we assist you?
Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
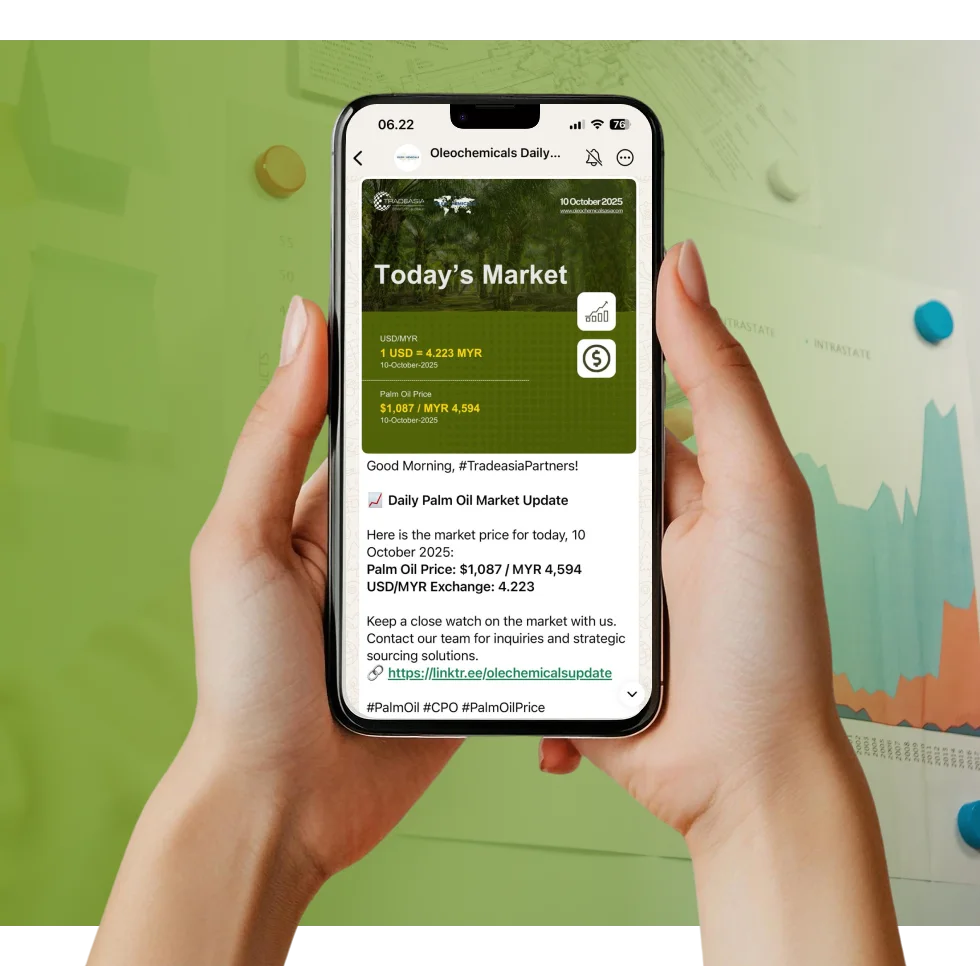
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Log in now to access technical product documents from our product range.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home All Products Toilet Soap Noodles TFM ±79% (80:20)
|
Origin |
: Indonesia |
|
IUPAC Name |
: N/A |
|
Cas Number |
: 143-07-7 |
|
HS Code |
: 3401.20.20 |
|
Formula |
: N/A |
|
Appearance Name |
: White Solid |
|
Common Names |
: Soap Chips |
|
Packaging |
: 25 Kg – Laminated Bags |
For more detailed information including pricing, customization, and shipping:
Brief Overview
Making soap noodles requires the saponification process using sodium hydroxide to saponify vegetable oils including palm, coconut, olive, and/or animal fat (tallow). One of the earliest known types of soap is soap noodles. The majority of soap producers utilize soap noodles because they create soap more quickly, even when flavors, colors, and other ingredients are modified. It is possible to modify the finished soap product by using further procedures like pressing, stamping, and molding.
Manufacturing Process
In the primary soap-making method, triglyceride molecules undergo direct saponification with sodium hydroxide. Hydrolysis breaks down fats and oils into glycerol and fatty acids. The ensuing step involves the neutralization of fatty acids using sodium hydroxide. Methanol is employed for the trans-esterification of the oil or fat, generating methyl esters, which are then saponified with sodium hydroxide to yield soap, accompanied by methanol as a byproduct.
Detergent Industry
The mixture is introduced into a worm screw or processed with rollers to form a thin soap sheet. Applying high pressure, the liquid is stirred along the screw's length, extruding numerous soap layers through a perforated endplate. Using a large worm screw extruder, also known as a plodder, the homogenized soap is compressed to produce a continuous soap bar.
Diverse soap noodles' specifications enable the creation of various soaps, such as medicinal, high-lather, transparent, laundry, and toilet soap.
How can we assist you?
