How can we assist you?
Explore our network of country and industry based websites to access localized information, product offerings, and business services across our group.
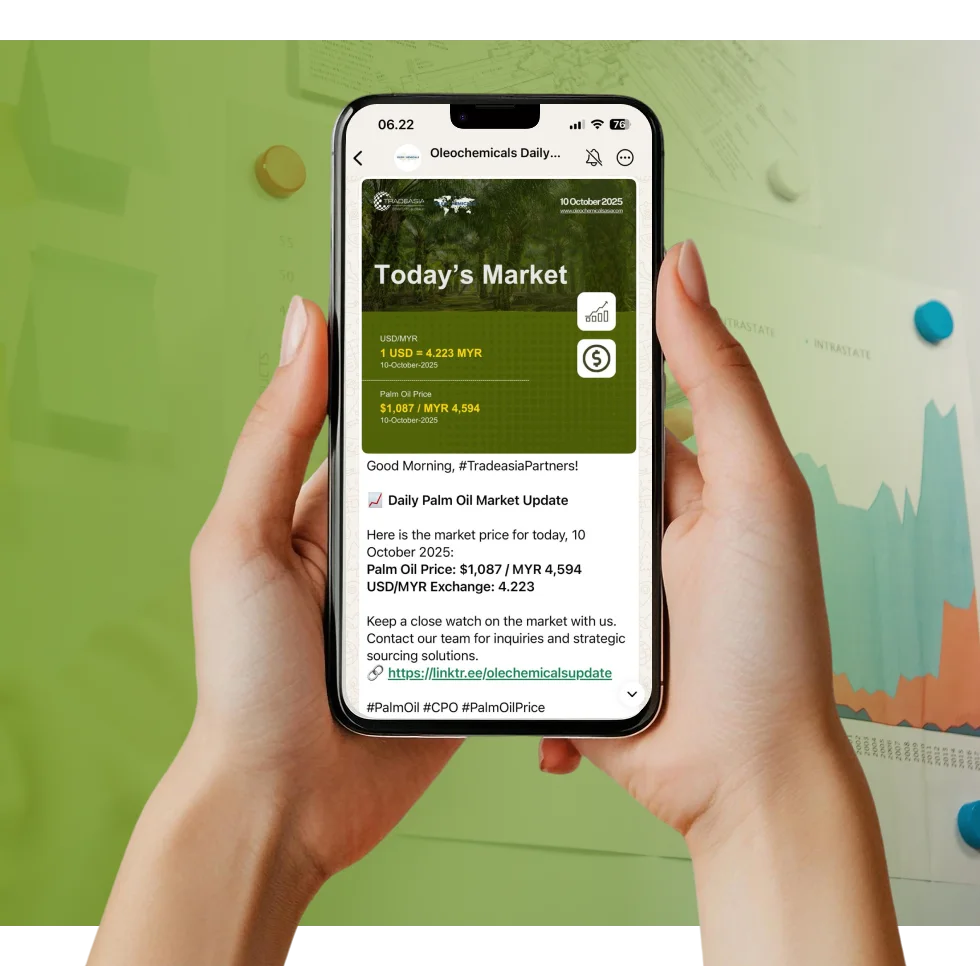
Access reliable chemical market information through our update channels.
Real-time Updates
Daily Updates
Log in to start sending quotation requests for any product.
Don't have an account? Sign Up Here
Home Enzymatic Breakthroughs in Palm Oil R&D
Market Insight | Insight | 25 August 2025
Oleochemicals

Breakthroughs in enzymatic technology are reshaping palm oil research and development, creating new opportunities for value-added products and sustainable growth. Biocatalysis, led by the use of lipases as powerful catalysts, is enabling palm oil to be converted into high-value derivatives such as fatty acid esters, biodiesel, and specialty oleochemicals. These advancements not only improve efficiency but also align with the industry’s long-term sustainability objectives.
Lipase-driven processes such as esterification, transesterification, and interesterification are proving pivotal. In biodiesel production, for example, lipases enable transesterification of triglycerides under milder operating conditions than traditional alkaline catalysts. This results in higher product purity, stronger yields, and lower energy requirements—directly improving process economics. A notable case is the use of immobilized lipase from Candida antarctica, which has achieved biodiesel yields of over 80% under ultrasonic conditions while generating valuable byproducts like triacetin, enhancing profitability. Although enzyme stability and reusability remain development priorities, the business case for enzymatic approaches continues to strengthen.
Compared with conventional chemical catalysis, enzymes deliver significant operational advantages. Their high selectivity reduces side reactions, lowers energy costs, and minimizes hazardous waste generation. They also simplify downstream purification, making byproduct management more cost-efficient—particularly when separating glycerol in biodiesel production. Beyond cost savings, these process improvements provide clear sustainability gains, a key driver for global market adoption. Ongoing R&D efforts are now focused on creating enzymes with greater durability and longer operational lifespans, which will further reduce costs and expand industrial feasibility.
The period of 2024–2025 has demonstrated the commercial potential of integrated systems combining enzymatic and chemical processes. Recent studies show that continuous-flow technologies, when coupled with lipase catalysis, can deliver exceptional results. For instance, a process utilizing Candida rugosa lipase achieved over 99% conversion of canola oil triglycerides under both batch and continuous-flow conditions, followed by catalytic upgrades producing renewable hydrocarbons. These approaches significantly cut reaction times and energy use, offering greener and more efficient alternatives that are highly relevant for future palm oil applications.
From a market perspective, the opportunities are substantial. Global palm oil production remains above 70 million metric tons annually, providing a robust foundation for further downstream innovation. The oleochemical market alone is projected to exceed USD 30 billion by the mid-2020s, with rising demand for environmentally friendly biofuels and specialty chemicals driving investment in biocatalysis. By leveraging enzymatic technology, companies can expand palm oil’s product portfolio, diversify revenue streams, and strengthen alignment with international sustainability commitments.
In summary, enzymatic breakthroughs are creating a competitive advantage for palm oil players by opening new pathways to higher-value, lower-carbon products. Lipases and other biocatalysts are delivering efficiency gains, cost reductions, and environmental benefits, while integrated continuous-flow systems are accelerating scalability. With enzyme stability improving and market demand increasing, enzymatic biocatalysis is positioned to become a cornerstone technology—supporting both profitability and sustainability across the global oleochemical sector.
We're committed to your privacy. Tradeasia uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. For more information, check out our privacy policy.
How can we assist you?
